Anthropic Chat
Anthropic Claude 是一个基础 AI 模型家族,可用于各种应用。对于开发者和企业,您可以利用 API 访问直接在 Anthropic 的 AI 基础设施之上构建应用。
Spring AI 支持 Anthropic Messaging API,用于同步和流式文本生成。
| Anthropic 的 Claude 模型也可以通过 Amazon Bedrock Converse 获得。Spring AI 也提供了专门的 Amazon Bedrock Converse Anthropic 客户端实现。 |
先决条件
您需要在 Anthropic 门户上创建一个 API 密钥。
在 Anthropic API 控制台 创建一个帐户,并在 获取 API 密钥 页面生成 API 密钥。
Spring AI 项目定义了一个名为 spring.ai.anthropic.api-key 的配置属性,您应该将其设置为从 anthropic.com 获取的 API 密钥 值。
您可以在 application.properties 文件中设置此配置属性
spring.ai.anthropic.api-key=<your-anthropic-api-key>为了在处理敏感信息(如 API 密钥)时增强安全性,您可以使用 Spring Expression Language (SpEL) 引用自定义环境变量
# In application.yml
spring:
ai:
anthropic:
api-key: ${ANTHROPIC_API_KEY}# In your environment or .env file
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=<your-anthropic-api-key>您也可以在应用程序代码中以编程方式获取此配置
// Retrieve API key from a secure source or environment variable
String apiKey = System.getenv("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY");自动配置
|
Spring AI 自动配置、启动模块的工件名称发生了重大变化。请参阅 升级说明 以获取更多信息。 |
Spring AI 为 Anthropic Chat 客户端提供了 Spring Boot 自动配置。要启用它,请将以下依赖项添加到项目的 Maven pom.xml 或 Gradle build.gradle 文件中
-
Maven
-
Gradle
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-anthropic</artifactId>
</dependency>dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-starter-model-anthropic'
}| 请参阅 依赖项管理 部分,将 Spring AI BOM 添加到您的构建文件中。 |
聊天属性
重试属性
前缀 spring.ai.retry 用作属性前缀,可让您配置 Anthropic 聊天模型的重试机制。
| 财产 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
spring.ai.retry.max-attempts |
最大重试次数。 |
10 |
spring.ai.retry.backoff.initial-interval |
指数回退策略的初始休眠时间。 |
2 秒。 |
spring.ai.retry.backoff.multiplier |
回退间隔乘数。 |
5 |
spring.ai.retry.backoff.max-interval |
最大回退持续时间。 |
3 分钟。 |
spring.ai.retry.on-client-errors |
如果为 false,则抛出 NonTransientAiException,并且不尝试重试 |
假 |
spring.ai.retry.exclude-on-http-codes |
不应触发重试的 HTTP 状态代码列表(例如,抛出 NonTransientAiException)。 |
空 |
spring.ai.retry.on-http-codes |
应触发重试的 HTTP 状态代码列表(例如,抛出 TransientAiException)。 |
空 |
| 目前,重试策略不适用于流式 API。 |
连接属性
前缀 spring.ai.anthropic 用作属性前缀,可让您连接到 Anthropic。
| 财产 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
spring.ai.anthropic.base-url |
要连接的 URL |
|
spring.ai.anthropic.completions-path |
要附加到基本 URL 的路径。 |
|
spring.ai.anthropic.version |
Anthropic API 版本 |
2023-06-01 |
spring.ai.anthropic.api-key |
API 密钥 |
- |
spring.ai.anthropic.beta-version |
启用新/实验性功能。如果设置为 |
|
配置属性
|
聊天自动配置的启用和禁用现在通过以 要启用,请设置 spring.ai.model.chat=anthropic(默认已启用) 要禁用,请设置 spring.ai.model.chat=none(或任何与 anthropic 不匹配的值) 此更改是为了允许配置多个模型。 |
前缀 spring.ai.anthropic.chat 是属性前缀,用于配置 Anthropic 的聊天模型实现。
| 财产 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.enabled (已移除且不再有效) |
启用 Anthropic 聊天模型。 |
true |
spring.ai.model.chat |
启用 Anthropic 聊天模型。 |
anthropic |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.model |
这是要使用的 Anthropic Chat 模型。支持: |
|
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.temperature |
用于控制生成完成的明显创造性的采样温度。较高的值将使输出更随机,而较低的值将使结果更集中和确定。不建议在同一完成请求中修改温度和 top_p,因为这两个设置的相互作用难以预测。 |
0.8 |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.max-tokens |
在聊天完成中生成的最大令牌数。输入令牌和生成令牌的总长度受模型的上下文长度限制。 |
500 |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.stop-sequence |
自定义文本序列,将导致模型停止生成。我们的模型通常会在自然完成其回合时停止,这将导致响应 stop_reason 为 "end_turn"。如果您希望模型在遇到自定义字符串时停止生成,可以使用 stop_sequences 参数。如果模型遇到其中一个自定义序列,则响应 stop_reason 值为 "stop_sequence",响应 stop_sequence 值将包含匹配的停止序列。 |
- |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.top-p |
使用核采样。在核采样中,我们以递减的概率顺序计算每个后续令牌的所有选项的累积分布,并在达到 top_p 指定的特定概率时将其截断。您应该修改 temperature 或 top_p,但不要同时修改两者。仅推荐用于高级用例。您通常只需要使用 temperature。 |
- |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.top-k |
仅从每个后续令牌的前 K 个选项中采样。用于删除“长尾”低概率响应。在此处了解更多技术细节。仅推荐用于高级用例。您通常只需要使用 temperature。 |
- |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.tool-names |
工具列表,通过其名称标识,用于在单个提示请求中启用工具调用。具有这些名称的工具必须存在于 toolCallbacks 注册表中。 |
- |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.tool-callbacks |
要注册到 ChatModel 的工具回调。 |
- |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.toolChoice |
控制模型调用哪个(如果有)工具。 |
- |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.internal-tool-execution-enabled |
如果为 false,Spring AI 将不会在内部处理工具调用,而是将其代理到客户端。然后,客户端负责处理工具调用,将其分派到适当的函数,并返回结果。如果为 true(默认),Spring AI 将在内部处理函数调用。仅适用于支持函数调用的聊天模型 |
true |
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.http-headers |
要添加到聊天完成请求的可选 HTTP 标头。 |
- |
| 有关模型别名及其描述的最新列表,请参阅 Anthropic 官方模型别名文档。 |
所有以 spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options 为前缀的属性都可以在运行时通过向 Prompt 调用添加请求特定的 运行时选项 来覆盖。 |
运行时选项
AnthropicChatOptions.java 提供了模型配置,例如要使用的模型、温度、最大令牌计数等。
在启动时,可以使用 AnthropicChatModel(api, options) 构造函数或 spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.* 属性配置默认选项。
在运行时,您可以通过向 Prompt 调用添加新的、请求特定的选项来覆盖默认选项。例如,为特定请求覆盖默认模型和温度
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"Generate the names of 5 famous pirates.",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-3-7-sonnet-latest")
.temperature(0.4)
.build()
));| 除了特定于模型的 AnthropicChatOptions 之外,您还可以使用通过 ChatOptions#builder() 创建的可移植 ChatOptions 实例。 |
提示缓存
Anthropic 的 提示缓存功能 允许您缓存常用提示,以降低成本并缩短重复交互的响应时间。当您缓存一个提示时,后续相同的请求可以重用缓存的内容,从而显著减少处理的输入令牌数量。
|
支持的模型 提示缓存目前支持 Claude Opus 4、Claude Sonnet 4、Claude Sonnet 3.7、Claude Sonnet 3.5、Claude Haiku 3.5、Claude Haiku 3 和 Claude Opus 3。 令牌要求 不同的模型对缓存效率有不同的最小令牌阈值:- Claude Sonnet 4:1024+ 令牌 - Claude Haiku 模型:2048+ 令牌 - 其他模型:1024+ 令牌 |
缓存策略
Spring AI 通过 AnthropicCacheStrategy 枚举提供战略性缓存放置。每个策略都会自动在最佳位置放置缓存断点,同时保持在 Anthropic 的 4 个断点限制内。
| 策略 | 使用的断点 | 用例 |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
完全禁用提示缓存。当请求是一次性的或内容太小无法从缓存中受益时使用。 |
|
1 |
缓存系统消息内容。工具通过 Anthropic 的自动 ~20 块回溯机制隐式缓存。当系统提示很大且稳定,且工具少于 20 个时使用。 |
|
1 |
仅缓存工具定义。系统消息保持未缓存状态,并在每次请求时重新处理。当工具定义很大且稳定(5000+ 令牌),但系统提示频繁更改或根据租户/上下文而异时使用。 |
|
2 |
明确缓存工具定义(断点 1)和系统消息(断点 2)。当您有 20 多个工具(超出自动回溯)或希望对这两个组件进行确定性缓存时使用。系统更改不会使工具缓存失效。 |
|
1-4 |
缓存直至当前用户问题的所有对话历史记录。用于具有聊天记忆的多轮对话,其中对话历史记录随时间增长。 |
由于 Anthropic 的级联失效,更改工具定义将使所有下游缓存断点(系统、消息)失效。当使用 SYSTEM_AND_TOOLS 或 CONVERSATION_HISTORY 策略时,工具的稳定性至关重要。 |
启用提示缓存
通过在 AnthropicChatOptions 上设置 cacheOptions 并选择 strategy 来启用提示缓存。
仅系统缓存
最适合:稳定的系统提示,工具少于 20 个(工具通过自动回溯隐式缓存)。
// Cache system message content (tools cached implicitly)
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage("You are a helpful AI assistant with extensive knowledge..."),
new UserMessage("What is machine learning?")
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_ONLY)
.build())
.maxTokens(500)
.build()
)
);仅工具缓存
最适合:大型稳定工具集与动态系统提示(多租户应用,A/B 测试)。
// Cache tool definitions, system prompt processed fresh each time
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage("You are a " + persona + " assistant..."), // Dynamic per-tenant
new UserMessage("What's the weather like in San Francisco?")
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.TOOLS_ONLY)
.build())
.toolCallbacks(weatherToolCallback) // Large tool set cached
.maxTokens(500)
.build()
)
);系统和工具缓存
最适合:20 多个工具(超出自动回溯)或当两个组件都应独立缓存时。
// Cache both tool definitions and system message with independent breakpoints
// Changing system won't invalidate tool cache (but changing tools invalidates both)
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage("You are a weather analysis assistant..."),
new UserMessage("What's the weather like in San Francisco?")
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_AND_TOOLS)
.build())
.toolCallbacks(weatherToolCallback) // 20+ tools
.maxTokens(500)
.build()
)
);对话历史缓存
// Cache conversation history with ChatClient and memory (cache breakpoint on last user message)
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultSystem("You are a personalized career counselor...")
.defaultAdvisors(MessageChatMemoryAdvisor.builder(chatMemory)
.conversationId(conversationId)
.build())
.build();
String response = chatClient.prompt()
.user("What career advice would you give me?")
.options(AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.CONVERSATION_HISTORY)
.build())
.maxTokens(500)
.build())
.call()
.content();使用 ChatClient Fluent API
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt()
.system("You are an expert document analyst...")
.user("Analyze this large document: " + document)
.options(AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_ONLY)
.build())
.build())
.call()
.content();高级缓存选项
每消息 TTL(5 分钟或 1 小时)
默认情况下,缓存内容使用 5 分钟的 TTL。您可以为特定消息类型设置 1 小时的 TTL。当使用 1 小时 TTL 时,Spring AI 会自动设置所需的 Anthropic beta 标头。
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(new SystemMessage(largeSystemPrompt)),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_ONLY)
.messageTypeTtl(MessageType.SYSTEM, AnthropicCacheTtl.ONE_HOUR)
.build())
.maxTokens(500)
.build()
)
);扩展 TTL 使用 Anthropic beta 功能 extended-cache-ttl-2025-04-11。 |
缓存资格过滤器
通过设置最小内容长度和可选的基于令牌的长度函数来控制何时使用缓存断点
AnthropicCacheOptions cache = AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.CONVERSATION_HISTORY)
.messageTypeMinContentLength(MessageType.SYSTEM, 1024)
.messageTypeMinContentLength(MessageType.USER, 1024)
.messageTypeMinContentLength(MessageType.ASSISTANT, 1024)
.contentLengthFunction(text -> MyTokenCounter.count(text))
.build();
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(/* messages */),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(cache)
.build()
)
);如果使用 SYSTEM_AND_TOOLS 策略,无论内容长度如何,工具定义始终被考虑进行缓存。 |
使用示例
这是一个演示提示缓存和成本跟踪的完整示例
// Create system content that will be reused multiple times
String largeSystemPrompt = "You are an expert software architect specializing in distributed systems...";
// First request - creates cache
ChatResponse firstResponse = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage(largeSystemPrompt),
new UserMessage("What is microservices architecture?")
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_ONLY)
.build())
.maxTokens(500)
.build()
)
);
// Access cache-related token usage
AnthropicApi.Usage firstUsage = (AnthropicApi.Usage) firstResponse.getMetadata()
.getUsage().getNativeUsage();
System.out.println("Cache creation tokens: " + firstUsage.cacheCreationInputTokens());
System.out.println("Cache read tokens: " + firstUsage.cacheReadInputTokens());
// Second request with same system prompt - reads from cache
ChatResponse secondResponse = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage(largeSystemPrompt),
new UserMessage("What are the benefits of event sourcing?")
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_ONLY)
.build())
.maxTokens(500)
.build()
)
);
AnthropicApi.Usage secondUsage = (AnthropicApi.Usage) secondResponse.getMetadata()
.getUsage().getNativeUsage();
System.out.println("Cache creation tokens: " + secondUsage.cacheCreationInputTokens()); // Should be 0
System.out.println("Cache read tokens: " + secondUsage.cacheReadInputTokens()); // Should be > 0令牌使用跟踪
Usage 记录提供了有关缓存相关令牌消耗的详细信息。要访问 Anthropic 特定的缓存指标,请使用 getNativeUsage() 方法
AnthropicApi.Usage usage = (AnthropicApi.Usage) response.getMetadata()
.getUsage().getNativeUsage();缓存特定指标包括
-
cacheCreationInputTokens():返回创建缓存条目时使用的令牌数 -
cacheReadInputTokens():返回从现有缓存条目读取的令牌数
当您首次发送缓存的提示时:- cacheCreationInputTokens() 将大于 0 - cacheReadInputTokens() 将为 0
当您再次发送相同的缓存提示时:- cacheCreationInputTokens() 将为 0 - cacheReadInputTokens() 将大于 0
实际用例
法律文件分析
通过在多个问题中缓存文档内容,高效分析大型法律合同或合规文档
// Load a legal contract (PDF or text)
String legalContract = loadDocument("merger-agreement.pdf"); // ~3000 tokens
// System prompt with legal expertise
String legalSystemPrompt = "You are an expert legal analyst specializing in corporate law. " +
"Analyze the following contract and provide precise answers about terms, obligations, and risks: " +
legalContract;
// First analysis - creates cache
ChatResponse riskAnalysis = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage(legalSystemPrompt),
new UserMessage("What are the key termination clauses and associated penalties?")
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_ONLY)
.build())
.maxTokens(1000)
.build()
)
);
// Subsequent questions reuse cached document - 90% cost savings
ChatResponse obligationAnalysis = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage(legalSystemPrompt), // Same content - cache hit
new UserMessage("List all financial obligations and payment schedules.")
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_ONLY)
.build())
.maxTokens(1000)
.build()
)
);批量代码审查
使用一致的审查标准处理多个代码文件,同时缓存审查指南
// Define comprehensive code review guidelines
String reviewGuidelines = """
You are a senior software engineer conducting code reviews. Apply these criteria:
- Security vulnerabilities and best practices
- Performance optimizations and memory usage
- Code maintainability and readability
- Testing coverage and edge cases
- Design patterns and architecture compliance
""";
List<String> codeFiles = Arrays.asList(
"UserService.java", "PaymentController.java", "SecurityConfig.java"
);
List<String> reviews = new ArrayList<>();
for (String filename : codeFiles) {
String sourceCode = loadSourceFile(filename);
ChatResponse review = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage(reviewGuidelines), // Cached across all reviews
new UserMessage("Review this " + filename + " code:\n\n" + sourceCode)
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_ONLY)
.build())
.maxTokens(800)
.build()
)
);
reviews.add(review.getResult().getOutput().getText());
}
// Guidelines cached after first request, subsequent reviews are faster and cheaper具有共享工具的多租户 SaaS
构建一个多租户应用程序,其中工具是共享的,但系统提示是根据每个租户定制的
// Define large shared tool set (used by all tenants)
List<FunctionCallback> sharedTools = Arrays.asList(
weatherToolCallback, // ~500 tokens
calendarToolCallback, // ~800 tokens
emailToolCallback, // ~700 tokens
analyticsToolCallback, // ~600 tokens
reportingToolCallback, // ~900 tokens
// ... 20+ more tools, totaling 5000+ tokens
);
@Service
public class MultiTenantAIService {
public String handleTenantRequest(String tenantId, String userQuery) {
// Get tenant-specific configuration
TenantConfig config = tenantRepository.findById(tenantId);
// Dynamic system prompt per tenant
String tenantSystemPrompt = String.format("""
You are %s's AI assistant. Company values: %s.
Brand voice: %s. Compliance requirements: %s.
""", config.companyName(), config.values(),
config.brandVoice(), config.compliance());
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage(tenantSystemPrompt), // Different per tenant, NOT cached
new UserMessage(userQuery)
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.TOOLS_ONLY) // Cache tools only
.build())
.toolCallbacks(sharedTools) // Cached once, shared across all tenants
.maxTokens(800)
.build()
)
);
return response.getResult().getOutput().getText();
}
}
// Tools cached once (5000 tokens @ 10% = 500 token cost for cache hits)
// Each tenant's unique system prompt processed fresh (200-500 tokens @ 100%)
// Total per request: ~700-1000 tokens vs 5500+ without TOOLS_ONLY具有知识库的客户支持
创建一个客户支持系统,缓存您的产品知识库以获得一致、准确的响应
// Load comprehensive product knowledge
String knowledgeBase = """
PRODUCT DOCUMENTATION:
- API endpoints and authentication methods
- Common troubleshooting procedures
- Billing and subscription details
- Integration guides and examples
- Known issues and workarounds
""" + loadProductDocs(); // ~2500 tokens
@Service
public class CustomerSupportService {
public String handleCustomerQuery(String customerQuery, String customerId) {
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
List.of(
new SystemMessage("You are a helpful customer support agent. " +
"Use this knowledge base to provide accurate solutions: " + knowledgeBase),
new UserMessage("Customer " + customerId + " asks: " + customerQuery)
),
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.cacheOptions(AnthropicCacheOptions.builder()
.strategy(AnthropicCacheStrategy.SYSTEM_ONLY)
.build())
.maxTokens(600)
.build()
)
);
return response.getResult().getOutput().getText();
}
}
// Knowledge base is cached across all customer queries
// Multiple support agents can benefit from the same cached content最佳实践
-
选择正确的策略:
-
对于稳定的系统提示和少于 20 个工具(工具通过自动回溯隐式缓存),请使用
SYSTEM_ONLY -
对于大型稳定工具集(5000+ 令牌)和动态系统提示(多租户,A/B 测试),请使用
TOOLS_ONLY -
当您有 20 多个工具(超出自动回溯)或希望两者都独立缓存时,请使用
SYSTEM_AND_TOOLS -
对于多轮对话,请将
CONVERSATION_HISTORY与 ChatClient 内存一起使用 -
使用
NONE显式禁用缓存
-
-
了解级联失效:Anthropic 的缓存层次结构(
工具 → 系统 → 消息)意味着更改向下流动-
更改工具使以下内容失效:工具 + 系统 + 消息(所有缓存)❌❌❌
-
更改系统使以下内容失效:系统 + 消息(工具缓存保持有效)✅❌❌
-
更改消息使以下内容失效:仅消息(工具和系统缓存保持有效)✅✅❌
**Tool stability is critical** when using `SYSTEM_AND_TOOLS` or `CONVERSATION_HISTORY` strategies.
-
-
SYSTEM_AND_TOOLS 独立性:使用
SYSTEM_AND_TOOLS时,更改系统消息不会使工具缓存失效,即使系统提示不同,也能高效重用缓存的工具。 -
满足令牌要求:专注于缓存满足最小令牌要求的内容(Sonnet 4 为 1024+ 令牌,Haiku 模型为 2048+ 令牌)。
-
重用相同内容:缓存对提示内容的完全匹配效果最佳。即使是微小的更改也需要新的缓存条目。
-
监控令牌使用情况:使用缓存使用统计信息跟踪缓存效率:
java AnthropicApi.Usage usage = (AnthropicApi.Usage) response.getMetadata().getUsage().getNativeUsage(); if (usage != null) { System.out.println("缓存创建: " + usage.cacheCreationInputTokens()); System.out.println("缓存读取: " + usage.cacheReadInputTokens()); } -
战略性缓存放置:实现会根据您选择的策略自动在最佳位置放置缓存断点,确保符合 Anthropic 的 4 个断点限制。
-
缓存生命周期:默认 TTL 为 5 分钟;通过
messageTypeTtl(…)为每种消息类型设置 1 小时 TTL。每次缓存访问都会重置计时器。 -
工具缓存限制:请注意,基于工具的交互可能不会在响应中提供缓存使用元数据。
实现细节
Spring AI 中的提示缓存实现遵循以下关键设计原则
-
战略性缓存放置:缓存断点根据所选策略自动放置在最佳位置,确保符合 Anthropic 的 4 个断点限制。
-
CONVERSATION_HISTORY将缓存断点放置在:工具(如果存在)、系统消息和最后一条用户消息上 -
这使得 Anthropic 的前缀匹配能够逐步缓存不断增长的对话历史
-
每个回合都建立在以前缓存的前缀之上,最大限度地提高缓存重用
-
-
提供商可移植性:缓存配置通过
AnthropicChatOptions而不是单个消息完成,从而在切换不同 AI 提供商时保持兼容性。 -
线程安全:缓存断点跟踪采用线程安全机制实现,以正确处理并发请求。
-
自动内容排序:实现确保 JSON 内容块和缓存控制的在线排序符合 Anthropic 的 API 要求。
-
聚合资格检查:对于
CONVERSATION_HISTORY,实现在确定组合内容是否满足缓存的最小令牌阈值时,会考虑最后约 20 个内容块中的所有消息类型(用户、助手、工具)。
思考
Anthropic Claude 模型支持“思考”功能,允许模型在提供最终答案之前显示其推理过程。此功能实现了更透明、更详细的问题解决,特别是对于需要逐步推理的复杂问题。
|
支持的模型 思考功能受以下 Claude 模型支持
模型能力
所有支持模型的 API 请求结构相同,但输出行为有所不同。 |
思考配置
要在任何受支持的 Claude 模型上启用思考,请在您的请求中包含以下配置
所需配置
-
添加
thinking对象:-
"type": "enabled" -
budget_tokens:推理的令牌限制(建议从 1024 开始)
-
-
令牌预算规则:
-
budget_tokens通常必须小于max_tokens -
Claude 可能会使用比分配更少的令牌
-
更大的预算会增加推理深度,但可能会影响延迟
-
当使用带有交错思考的工具时(仅限 Claude 4),此限制会放宽,但 Spring AI 尚不支持。
-
关键考虑
-
Claude 3.7 在响应中返回完整的思考内容
-
Claude 4 返回模型内部推理的摘要版本,以减少延迟并保护敏感内容
-
思考令牌是计费的,作为输出令牌的一部分(即使并非所有令牌都在响应中可见)
-
交错思考仅适用于 Claude 4 模型,并且需要 beta 标头
interleaved-thinking-2025-05-14
工具集成和交错思考
Claude 4 模型支持带有工具使用的交错思考,允许模型在工具调用之间进行推理。
|
当前的 Spring AI 实现分别支持基本思考和工具使用,但尚不支持带有工具使用的交错思考(思考在多个工具调用之间继续)。 |
有关带有工具使用的交错思考的详细信息,请参阅 Anthropic 文档。
非流式示例
以下是使用 ChatClient API 在非流式请求中启用思考的方法
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.create(chatModel);
// For Claude 3.7 Sonnet - explicit thinking configuration required
ChatResponse response = chatClient.prompt()
.options(AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-3-7-sonnet-latest")
.temperature(1.0) // Temperature should be set to 1 when thinking is enabled
.maxTokens(8192)
.thinking(AnthropicApi.ThinkingType.ENABLED, 2048) // Must be ≥1024 && < max_tokens
.build())
.user("Are there an infinite number of prime numbers such that n mod 4 == 3?")
.call()
.chatResponse();
// For Claude 4 models - thinking is enabled by default
ChatResponse response4 = chatClient.prompt()
.options(AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-opus-4-0")
.maxTokens(8192)
// No explicit thinking configuration needed
.build())
.user("Are there an infinite number of prime numbers such that n mod 4 == 3?")
.call()
.chatResponse();
// Process the response which may contain thinking content
for (Generation generation : response.getResults()) {
AssistantMessage message = generation.getOutput();
if (message.getText() != null) {
// Regular text response
System.out.println("Text response: " + message.getText());
}
else if (message.getMetadata().containsKey("signature")) {
// Thinking content
System.out.println("Thinking: " + message.getMetadata().get("thinking"));
System.out.println("Signature: " + message.getMetadata().get("signature"));
}
}流式示例
您也可以将思考与流式响应一起使用
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.create(chatModel);
// For Claude 3.7 Sonnet - explicit thinking configuration
Flux<ChatResponse> responseFlux = chatClient.prompt()
.options(AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-3-7-sonnet-latest")
.temperature(1.0)
.maxTokens(8192)
.thinking(AnthropicApi.ThinkingType.ENABLED, 2048)
.build())
.user("Are there an infinite number of prime numbers such that n mod 4 == 3?")
.stream();
// For Claude 4 models - thinking is enabled by default
Flux<ChatResponse> responseFlux4 = chatClient.prompt()
.options(AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-opus-4-0")
.maxTokens(8192)
// No explicit thinking configuration needed
.build())
.user("Are there an infinite number of prime numbers such that n mod 4 == 3?")
.stream();
// For streaming, you might want to collect just the text responses
String textContent = responseFlux.collectList()
.block()
.stream()
.map(ChatResponse::getResults)
.flatMap(List::stream)
.map(Generation::getOutput)
.map(AssistantMessage::getText)
.filter(text -> text != null && !text.isBlank())
.collect(Collectors.joining());工具/函数调用
您可以在 AnthropicChatModel 中注册自定义 Java 工具,并让 Anthropic Claude 模型智能地选择输出一个 JSON 对象,其中包含调用一个或多个已注册函数的参数。这是一种将 LLM 能力与外部工具和 API 连接的强大技术。阅读有关 工具调用 的更多信息。
工具选择
tool_choice 参数允许您控制模型如何使用提供的工具。此功能让您可以对工具执行行为进行细粒度控制。
有关完整的 API 详细信息,请参阅 Anthropic tool_choice 文档。
工具选择选项
Spring AI 通过 AnthropicApi.ToolChoice 接口提供了四种工具选择策略
-
ToolChoiceAuto(默认):模型自动决定是使用工具还是回复文本 -
ToolChoiceAny:模型必须使用至少一个可用工具 -
ToolChoiceTool:模型必须按名称使用特定工具 -
ToolChoiceNone:模型不能使用任何工具
使用示例
自动模式(默认行为)
让模型决定是否使用工具
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"What's the weather in San Francisco?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.toolChoice(new AnthropicApi.ToolChoiceAuto())
.toolCallbacks(weatherToolCallback)
.build()
)
);强制使用工具(任意)
要求模型至少使用一个工具
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"What's the weather?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.toolChoice(new AnthropicApi.ToolChoiceAny())
.toolCallbacks(weatherToolCallback, calculatorToolCallback)
.build()
)
);强制使用特定工具
要求模型按名称使用特定工具
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"What's the weather in San Francisco?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.toolChoice(new AnthropicApi.ToolChoiceTool("get_weather"))
.toolCallbacks(weatherToolCallback, calculatorToolCallback)
.build()
)
);禁用工具使用
阻止模型使用任何工具
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"What's the weather in San Francisco?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.toolChoice(new AnthropicApi.ToolChoiceNone())
.toolCallbacks(weatherToolCallback)
.build()
)
);禁用并行工具使用
强制模型一次只使用一个工具
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"What's the weather in San Francisco and what's 2+2?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.toolChoice(new AnthropicApi.ToolChoiceAuto(true)) // disableParallelToolUse = true
.toolCallbacks(weatherToolCallback, calculatorToolCallback)
.build()
)
);多模态
多模态是指模型同时理解和处理来自各种来源(包括文本、PDF、图像、数据格式)信息的能力。
图像
目前,Anthropic Claude 3 支持 images 的 base64 源类型,以及 image/jpeg、image/png、image/gif 和 image/webp 媒体类型。有关更多信息,请查看 视觉指南。Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet 还支持 application/pdf 文件的 pdf 源类型。
Spring AI 的 Message 接口通过引入 Media 类型支持多模态 AI 模型。此类型包含消息中媒体附件的数据和信息,使用 Spring 的 org.springframework.util.MimeType 和用于原始媒体数据的 java.lang.Object。
以下是从 AnthropicChatModelIT.java 中提取的一个简单代码示例,演示了用户文本与图像的组合。
var imageData = new ClassPathResource("/multimodal.test.png");
var userMessage = new UserMessage("Explain what do you see on this picture?",
List.of(new Media(MimeTypeUtils.IMAGE_PNG, this.imageData)));
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(new Prompt(List.of(this.userMessage)));
logger.info(response.getResult().getOutput().getContent());它以 multimodal.test.png 图像作为输入

以及文本消息“解释你在这张图片上看到了什么?”,并生成类似以下内容的响应
The image shows a close-up view of a wire fruit basket containing several pieces of fruit. ...
从 Sonnet 3.5 开始提供 PDF 支持 (beta)。使用 application/pdf 媒体类型将 PDF 文件附加到消息中
var pdfData = new ClassPathResource("/spring-ai-reference-overview.pdf");
var userMessage = new UserMessage(
"You are a very professional document summarization specialist. Please summarize the given document.",
List.of(new Media(new MimeType("application", "pdf"), pdfData)));
var response = this.chatModel.call(new Prompt(List.of(userMessage)));引文
Anthropic 的 引文 API 允许 Claude 在生成响应时引用所提供文档的特定部分。当提示中包含引文文档时,Claude 可以引用源材料,并且引文元数据(字符范围、页码或内容块)会作为响应元数据返回。
引文有助于提高
-
准确性验证:用户可以根据源材料验证 Claude 的响应
-
透明度:精确查看文档的哪些部分提供了响应信息
-
合规性:满足受监管行业中源归属的要求
-
信任:通过显示信息来源建立信任
|
支持的模型 引文支持 Claude 3.7 Sonnet 和 Claude 4 模型(Opus 和 Sonnet)。 文档类型 支持三种类型的引文文档
|
创建引文文档
使用 CitationDocument 构建器创建可引用的文档
纯文本文档
CitationDocument document = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText("The Eiffel Tower was completed in 1889 in Paris, France. " +
"It stands 330 meters tall and was designed by Gustave Eiffel.")
.title("Eiffel Tower Facts")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();PDF 文档
// From file path
CitationDocument document = CitationDocument.builder()
.pdfFile("path/to/document.pdf")
.title("Technical Specification")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();
// From byte array
byte[] pdfBytes = loadPdfBytes();
CitationDocument document = CitationDocument.builder()
.pdf(pdfBytes)
.title("Product Manual")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();自定义内容块
对于细粒度的引文控制,请使用自定义内容块
CitationDocument document = CitationDocument.builder()
.customContent(
"The Great Wall of China is approximately 21,196 kilometers long.",
"It was built over many centuries, starting in the 7th century BC.",
"The wall was constructed to protect Chinese states from invasions."
)
.title("Great Wall Facts")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();在请求中使用引文
在您的聊天选项中包含引文文档
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"When was the Eiffel Tower built and how tall is it?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-3-7-sonnet-latest")
.maxTokens(1024)
.citationDocuments(document)
.build()
)
);多个文档
您可以提供多个文档供 Claude 引用
CitationDocument parisDoc = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText("Paris is the capital city of France with a population of 2.1 million.")
.title("Paris Information")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();
CitationDocument eiffelDoc = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText("The Eiffel Tower was designed by Gustave Eiffel for the 1889 World's Fair.")
.title("Eiffel Tower History")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"What is the capital of France and who designed the Eiffel Tower?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-3-7-sonnet-latest")
.citationDocuments(parisDoc, eiffelDoc)
.build()
)
);访问引文
引文在响应元数据中返回
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(prompt);
// Get citations from metadata
List<Citation> citations = (List<Citation>) response.getMetadata().get("citations");
// Optional: Get citation count directly from metadata
Integer citationCount = (Integer) response.getMetadata().get("citationCount");
System.out.println("Total citations: " + citationCount);
// Process each citation
for (Citation citation : citations) {
System.out.println("Document: " + citation.getDocumentTitle());
System.out.println("Location: " + citation.getLocationDescription());
System.out.println("Cited text: " + citation.getCitedText());
System.out.println("Document index: " + citation.getDocumentIndex());
System.out.println();
}引文类型
引文包含不同的位置信息,具体取决于文档类型
字符位置(纯文本)
对于纯文本文档,引文包括字符索引
Citation citation = citations.get(0);
if (citation.getType() == Citation.LocationType.CHAR_LOCATION) {
int start = citation.getStartCharIndex();
int end = citation.getEndCharIndex();
String text = citation.getCitedText();
System.out.println("Characters " + start + "-" + end + ": " + text);
}页位置(PDF)
对于 PDF 文档,引文包括页码
Citation citation = citations.get(0);
if (citation.getType() == Citation.LocationType.PAGE_LOCATION) {
int startPage = citation.getStartPageNumber();
int endPage = citation.getEndPageNumber();
System.out.println("Pages " + startPage + "-" + endPage);
}内容块位置(自定义内容)
对于自定义内容,引文引用特定的内容块
Citation citation = citations.get(0);
if (citation.getType() == Citation.LocationType.CONTENT_BLOCK_LOCATION) {
int startBlock = citation.getStartBlockIndex();
int endBlock = citation.getEndBlockIndex();
System.out.println("Content blocks " + startBlock + "-" + endBlock);
}完整示例
这是一个演示引文使用的完整示例
// Create a citation document
CitationDocument document = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText("Spring AI is an application framework for AI engineering. " +
"It provides a Spring-friendly API for developing AI applications. " +
"The framework includes abstractions for chat models, embedding models, " +
"and vector databases.")
.title("Spring AI Overview")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();
// Call the model with the document
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"What is Spring AI?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-3-7-sonnet-latest")
.maxTokens(1024)
.citationDocuments(document)
.build()
)
);
// Display the response
System.out.println("Response: " + response.getResult().getOutput().getText());
System.out.println("\nCitations:");
// Process citations
List<Citation> citations = (List<Citation>) response.getMetadata().get("citations");
if (citations != null && !citations.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < citations.size(); i++) {
Citation citation = citations.get(i);
System.out.println("\n[" + (i + 1) + "] " + citation.getDocumentTitle());
System.out.println(" Location: " + citation.getLocationDescription());
System.out.println(" Text: " + citation.getCitedText());
}
} else {
System.out.println("No citations were provided in the response.");
}最佳实践
-
使用描述性标题:为引文文档提供有意义的标题,以帮助用户在引文中识别来源。
-
检查是否存在空引文:并非所有响应都将包含引文,因此在访问引文元数据之前始终验证其是否存在。
-
考虑文档大小:更大的文档提供更多上下文,但会消耗更多输入令牌并可能影响响应时间。
-
利用多个文档:当回答涉及多个来源的问题时,在单个请求中提供所有相关文档,而不是进行多次调用。
-
使用适当的文档类型:对于简单内容使用纯文本,对于现有文档使用 PDF,当您需要对引文粒度进行细粒度控制时使用自定义内容块。
实际用例
法律文件分析
在保持来源归属的同时分析合同和法律文档
CitationDocument contract = CitationDocument.builder()
.pdfFile("merger-agreement.pdf")
.title("Merger Agreement 2024")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"What are the key termination clauses in this contract?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.maxTokens(2000)
.citationDocuments(contract)
.build()
)
);
// Citations will reference specific pages in the PDF客户支持知识库
提供具有可验证来源的准确客户支持答案
CitationDocument kbArticle1 = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText(loadKnowledgeBaseArticle("authentication"))
.title("Authentication Guide")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();
CitationDocument kbArticle2 = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText(loadKnowledgeBaseArticle("billing"))
.title("Billing FAQ")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"How do I reset my password and update my billing information?",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-3-7-sonnet-latest")
.citationDocuments(kbArticle1, kbArticle2)
.build()
)
);
// Citations show which KB articles were referenced研究与合规
生成需要来源引文以符合合规性要求的报告
CitationDocument clinicalStudy = CitationDocument.builder()
.pdfFile("clinical-trial-results.pdf")
.title("Clinical Trial Phase III Results")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();
CitationDocument regulatoryGuidance = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText(loadRegulatoryDocument())
.title("FDA Guidance Document")
.citationsEnabled(true)
.build();
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(
new Prompt(
"Summarize the efficacy findings and regulatory implications.",
AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-sonnet-4")
.maxTokens(3000)
.citationDocuments(clinicalStudy, regulatoryGuidance)
.build()
)
);
// Citations provide audit trail for compliance引文文档选项
上下文字段
可选地提供有关文档的上下文,该上下文不会被引用,但可以指导 Claude 的理解
CitationDocument document = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText("...")
.title("Legal Contract")
.context("This is a merger agreement dated January 2024 between Company A and Company B")
.build();控制引文
默认情况下,所有文档的引文都已禁用(选择加入行为)。要启用引文,请显式设置 citationsEnabled(true)
CitationDocument document = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText("The Eiffel Tower was completed in 1889...")
.title("Historical Facts")
.citationsEnabled(true) // Explicitly enable citations for this document
.build();您还可以提供不带引文的文档作为背景上下文
CitationDocument backgroundDoc = CitationDocument.builder()
.plainText("Background information about the industry...")
.title("Context Document")
// citationsEnabled defaults to false - Claude will use this but not cite it
.build();|
Anthropic 要求请求中所有文档的引文设置一致。您不能在同一请求中混合使用启用引文和禁用引文的文档。 |
示例控制器
创建 一个新的 Spring Boot 项目,并将 spring-ai-starter-model-anthropic 添加到您的 pom (或 gradle) 依赖项中。
在 src/main/resources 目录下添加一个 application.properties 文件,以启用和配置 Anthropic 聊天模型
spring.ai.anthropic.api-key=YOUR_API_KEY
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.model=claude-3-5-sonnet-latest
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.temperature=0.7
spring.ai.anthropic.chat.options.max-tokens=450将 api-key 替换为您的 Anthropic 凭据。 |
这将创建一个 AnthropicChatModel 实现,您可以将其注入到您的类中。这是一个简单的 @Controller 类的示例,它使用聊天模型进行文本生成。
@RestController
public class ChatController {
private final AnthropicChatModel chatModel;
@Autowired
public ChatController(AnthropicChatModel chatModel) {
this.chatModel = chatModel;
}
@GetMapping("/ai/generate")
public Map generate(@RequestParam(value = "message", defaultValue = "Tell me a joke") String message) {
return Map.of("generation", this.chatModel.call(message));
}
@GetMapping("/ai/generateStream")
public Flux<ChatResponse> generateStream(@RequestParam(value = "message", defaultValue = "Tell me a joke") String message) {
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(new UserMessage(message));
return this.chatModel.stream(prompt);
}
}手动配置
AnthropicChatModel 实现了 ChatModel 和 StreamingChatModel,并使用 低级 AnthropicApi 客户端 连接到 Anthropic 服务。
将 spring-ai-anthropic 依赖项添加到您的项目的 Maven pom.xml 文件中
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-anthropic</artifactId>
</dependency>或添加到您的 Gradle build.gradle 构建文件中。
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.ai:spring-ai-anthropic'
}| 请参阅 依赖项管理 部分,将 Spring AI BOM 添加到您的构建文件中。 |
接下来,创建一个 AnthropicChatModel 并将其用于文本生成
var anthropicApi = new AnthropicApi(System.getenv("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"));
var anthropicChatOptions = AnthropicChatOptions.builder()
.model("claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219")
.temperature(0.4)
.maxTokens(200)
.build()
var chatModel = AnthropicChatModel.builder().anthropicApi(anthropicApi)
.defaultOptions(anthropicChatOptions).build();
ChatResponse response = this.chatModel.call(
new Prompt("Generate the names of 5 famous pirates."));
// Or with streaming responses
Flux<ChatResponse> response = this.chatModel.stream(
new Prompt("Generate the names of 5 famous pirates."));AnthropicChatOptions 提供了聊天请求的配置信息。AnthropicChatOptions.Builder 是一个流式选项构建器。
低级 AnthropicApi 客户端
AnthropicApi 提供了一个轻量级的 Java 客户端,用于 Anthropic Message API。
以下类图说明了 AnthropicApi 聊天接口和构建块
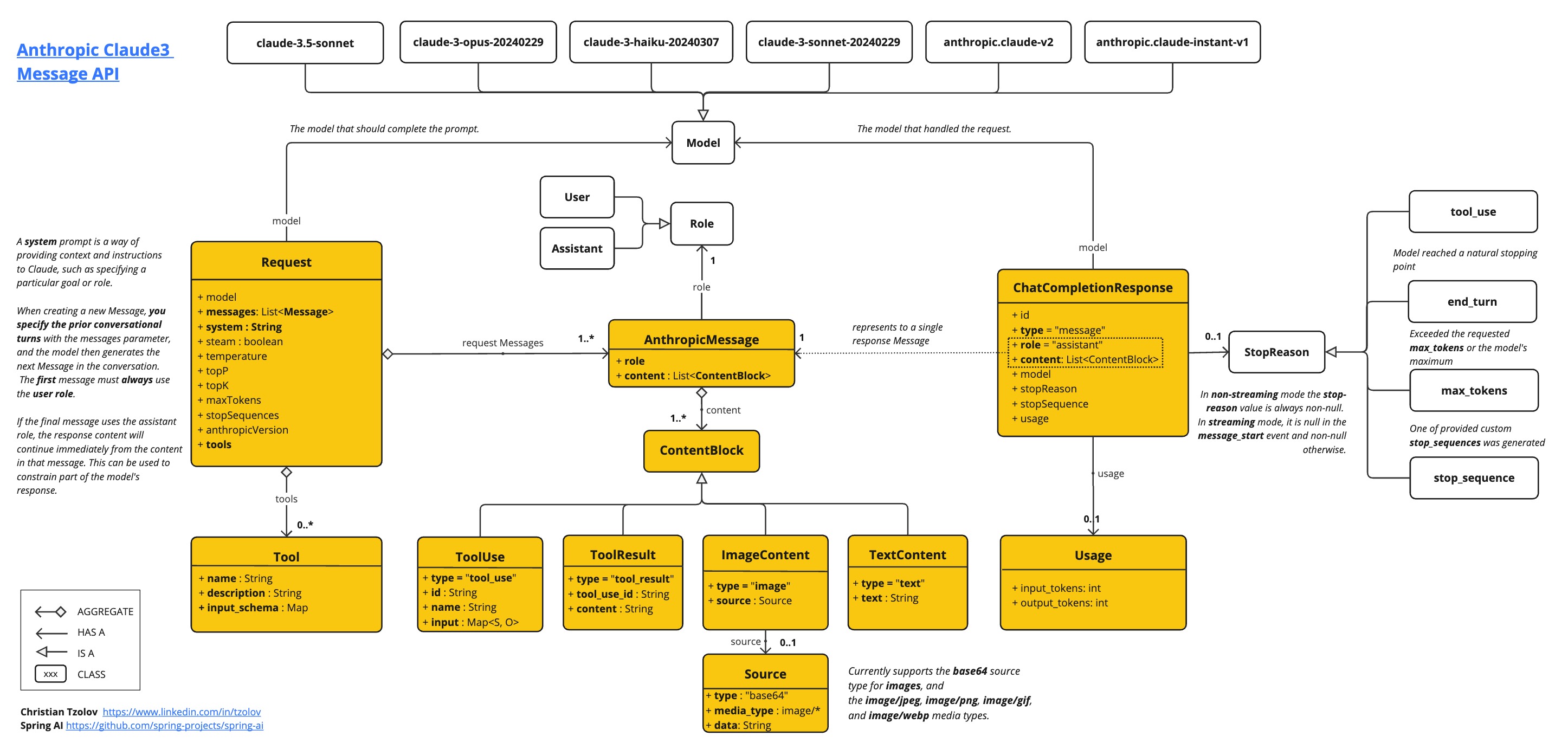
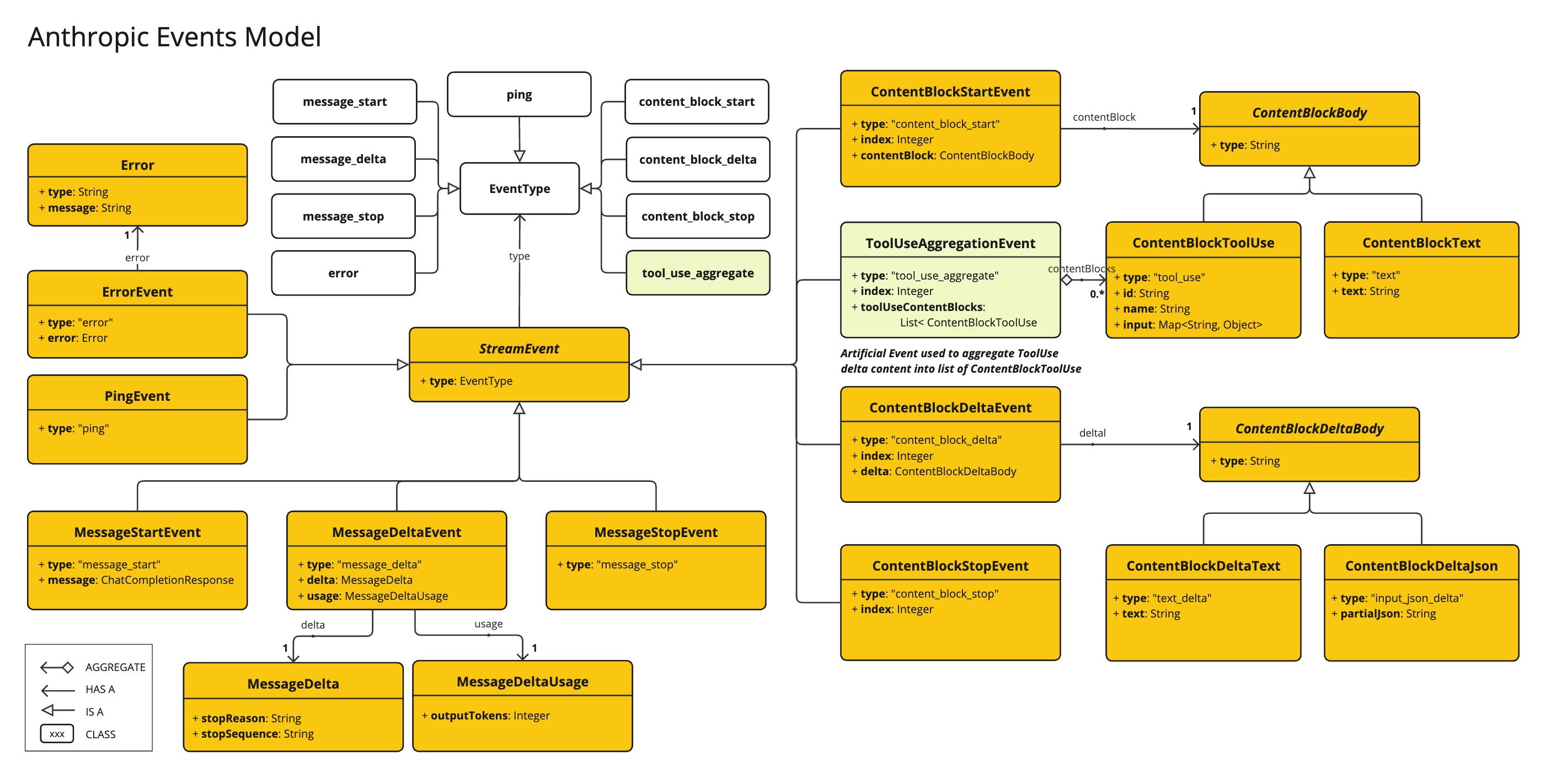
这是一个如何以编程方式使用 API 的简单片段
AnthropicApi anthropicApi =
new AnthropicApi(System.getenv("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"));
AnthropicMessage chatCompletionMessage = new AnthropicMessage(
List.of(new ContentBlock("Tell me a Joke?")), Role.USER);
// Sync request
ResponseEntity<ChatCompletionResponse> response = this.anthropicApi
.chatCompletionEntity(new ChatCompletionRequest(AnthropicApi.ChatModel.CLAUDE_3_OPUS.getValue(),
List.of(this.chatCompletionMessage), null, 100, 0.8, false));
// Streaming request
Flux<StreamResponse> response = this.anthropicApi
.chatCompletionStream(new ChatCompletionRequest(AnthropicApi.ChatModel.CLAUDE_3_OPUS.getValue(),
List.of(this.chatCompletionMessage), null, 100, 0.8, true));有关详细信息,请参阅 AnthropicApi.java 的 JavaDoc。
低级 API 示例
-
AnthropicApiIT.java 测试提供了一些如何使用轻量级库的通用示例。

