子元素
当此 Gateway 从 PollableChannel 接收消息时,您必须提供一个全局默认 Poller 或向 Job Launching Gateway 提供一个 Poller 子元素。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何在 Java 中提供 Poller
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "queueChannel", poller = @Poller(fixedRate="1000"))
public JobLaunchingGateway sampleJobLaunchingGateway() {
JobLaunchingGateway jobLaunchingGateway = new JobLaunchingGateway(jobLauncher());
jobLaunchingGateway.setOutputChannel(replyChannel());
return jobLaunchingGateway;
}以下示例展示了如何在 XML 中提供 Poller
<batch-int:job-launching-gateway request-channel="queueChannel"
reply-channel="replyChannel" job-launcher="jobLauncher">
<int:poller fixed-rate="1000">
</batch-int:job-launching-gateway>提供信息性消息的反馈
由于 Spring Batch job 可能运行很长时间,提供进度信息通常至关重要。例如,利益相关者可能希望在批处理 job 的部分或全部失败时收到通知。Spring Batch 通过以下方式支持收集此信息:
-
主动轮询
-
事件驱动的监听器
当异步启动 Spring Batch job 时(例如,通过使用 Job Launching Gateway),会返回一个 JobExecution 实例。因此,您可以使用 JobExecution.getJobId() 通过使用 JobExplorer 从 JobRepository 中检索更新的 JobExecution 实例来持续轮询状态更新。但是,这被认为是次优的,推荐使用事件驱动的方法。
因此,Spring Batch 提供了监听器,包括三种最常用的监听器:
-
StepListener -
ChunkListener -
JobExecutionListener
在下图所示的示例中,Spring Batch job 已配置了 StepExecutionListener。因此,Spring Integration 接收并处理任何 Step 执行前或执行后事件。例如,您可以使用 Router 检查收到的 StepExecution。根据检查结果,可以发生各种事情(例如,将消息路由到邮件出站通道适配器),以便可以根据某些条件发送电子邮件通知。
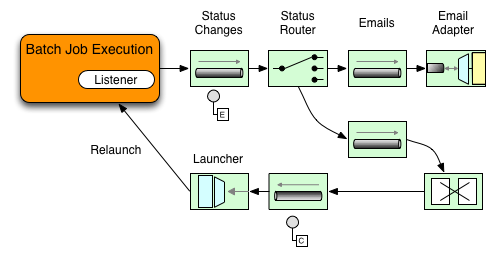
以下两部分示例展示了如何配置监听器以便将消息发送到用于 StepExecution 事件的 Gateway 并将其输出记录到 logging-channel-adapter。
首先,创建通知集成 bean。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何在 Java 中创建通知集成 bean
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "stepExecutionsChannel")
public LoggingHandler loggingHandler() {
LoggingHandler adapter = new LoggingHandler(LoggingHandler.Level.WARN);
adapter.setLoggerName("TEST_LOGGER");
adapter.setLogExpressionString("headers.id + ': ' + payload");
return adapter;
}
@MessagingGateway(name = "notificationExecutionsListener", defaultRequestChannel = "stepExecutionsChannel")
public interface NotificationExecutionListener extends StepExecutionListener {}您需要在配置中添加 @IntegrationComponentScan 注解。 |
以下示例展示了如何在 XML 中创建通知集成 bean
<int:channel id="stepExecutionsChannel"/>
<int:gateway id="notificationExecutionsListener"
service-interface="org.springframework.batch.core.StepExecutionListener"
default-request-channel="stepExecutionsChannel"/>
<int:logging-channel-adapter channel="stepExecutionsChannel"/>其次,修改您的 job 以添加 Step 级别的监听器。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何在 Java 中添加 Step 级别的监听器
public Job importPaymentsJob(JobRepository jobRepository, PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
return new JobBuilder("importPayments", jobRepository)
.start(new StepBuilder("step1", jobRepository)
.chunk(200, transactionManager)
.listener(notificationExecutionsListener())
// ...
.build();
)
.build();
}以下示例展示了如何在 XML 中添加 Step 级别的监听器
<job id="importPayments">
<step id="step1">
<tasklet ../>
<chunk ../>
<listeners>
<listener ref="notificationExecutionsListener"/>
</listeners>
</tasklet>
...
</step>
</job>异步处理器
异步处理器可帮助您扩展 Item 的处理能力。在异步处理器用例中,一个 AsyncItemProcessor 充当调度器,在新线程上执行 Item 的 ItemProcessor 逻辑。Item 完成后,将 Future 传递给 AsyncItemWriter 进行写入。
因此,您可以通过使用异步 Item 处理来提高性能,这基本上使您可以实现分叉-合并(fork-join)场景。一旦所有结果可用,AsyncItemWriter 就会收集结果并写回 Chunk。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何在 Java 中配置 AsyncItemProcessor
@Bean
public AsyncItemProcessor processor(ItemProcessor itemProcessor, TaskExecutor taskExecutor) {
AsyncItemProcessor asyncItemProcessor = new AsyncItemProcessor();
asyncItemProcessor.setTaskExecutor(taskExecutor);
asyncItemProcessor.setDelegate(itemProcessor);
return asyncItemProcessor;
}以下示例展示了如何在 XML 中配置 AsyncItemProcessor
<bean id="processor"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.async.AsyncItemProcessor">
<property name="delegate">
<bean class="your.ItemProcessor"/>
</property>
<property name="taskExecutor">
<bean class="org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor"/>
</property>
</bean>delegate 属性引用您的 ItemProcessor bean,而 taskExecutor 属性引用您选择的 TaskExecutor。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何在 Java 中配置 AsyncItemWriter
@Bean
public AsyncItemWriter writer(ItemWriter itemWriter) {
AsyncItemWriter asyncItemWriter = new AsyncItemWriter();
asyncItemWriter.setDelegate(itemWriter);
return asyncItemWriter;
}以下示例展示了如何在 XML 中配置 AsyncItemWriter
<bean id="itemWriter"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.async.AsyncItemWriter">
<property name="delegate">
<bean id="itemWriter" class="your.ItemWriter"/>
</property>
</bean>同样,delegate 属性实际上是您的 ItemWriter bean 的引用。
外部化批处理执行
到目前为止讨论的集成方法提出了 Spring Integration 像外壳一样包裹 Spring Batch 的用例。然而,Spring Batch 也可以在内部使用 Spring Integration。通过这种方法,Spring Batch 用户可以将 Item 甚至 Chunk 的处理委托给外部进程。这使您可以分载复杂的处理。Spring Batch Integration 为以下方面提供了专门的支持:
-
远程 Chunking
-
远程 Partitioning
远程 Chunking
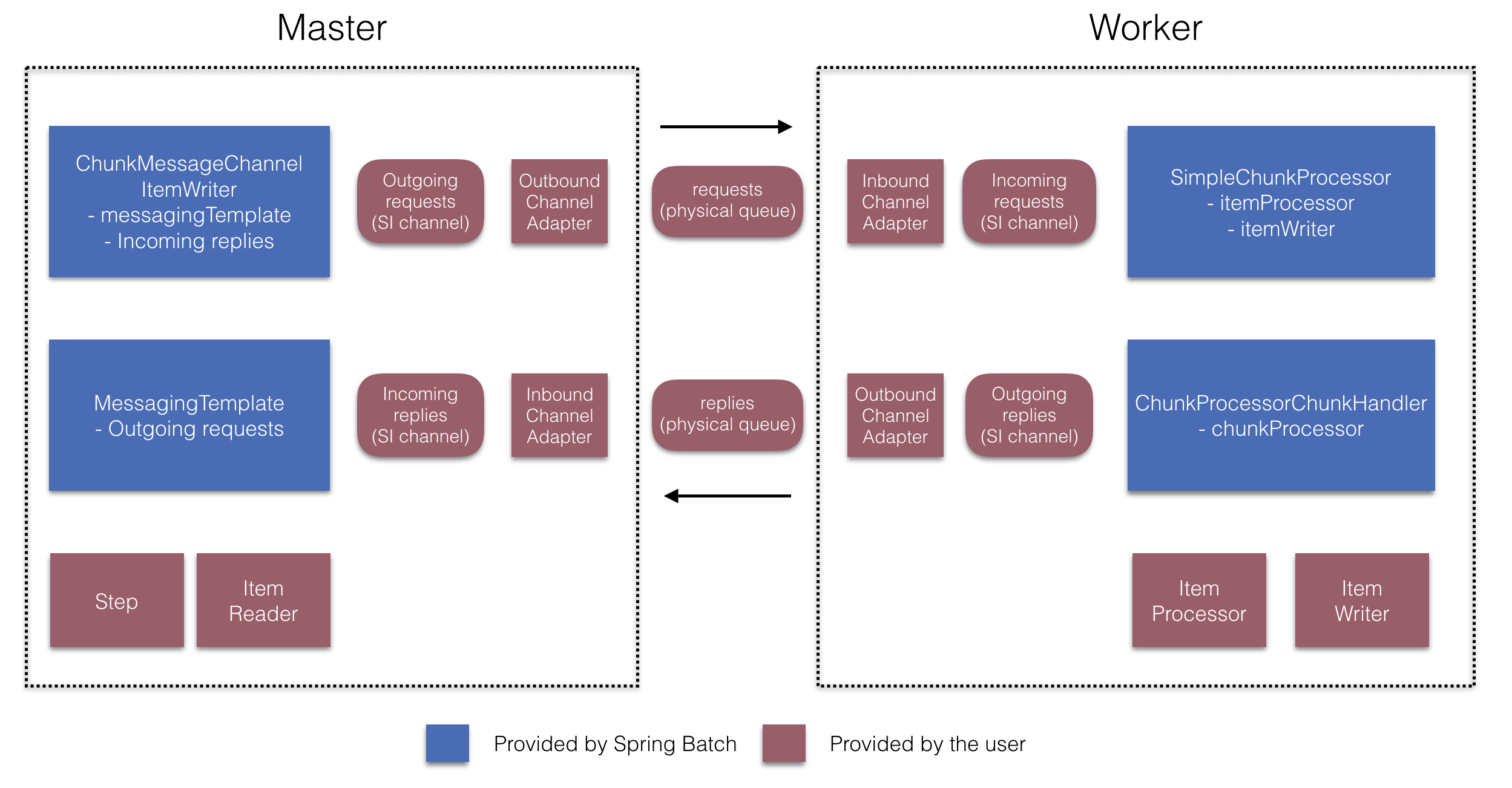
下图展示了将 Spring Batch 与 Spring Integration 一起使用时,远程 Chunking 工作的一种方式
更进一步,您还可以通过使用 ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter(由 Spring Batch Integration 提供)来外部化 Chunk 处理,它发送 Item 并收集结果。一旦发送,Spring Batch 会继续读取和分组 Item 的过程,而无需等待结果。相反,ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter 的责任是收集结果并将其集成回 Spring Batch 进程中。
使用 Spring Integration,您可以完全控制进程的并发性(例如,通过使用 QueueChannel 而不是 DirectChannel)。此外,通过依赖 Spring Integration 丰富的通道适配器集合(如 JMS 和 AMQP),您可以将批处理 Job 的 Chunk 分发到外部系统进行处理。
-
Java
-
XML
包含需要远程 Chunking 的 Step 的 Job 在 Java 中的配置可能与以下类似
public Job chunkJob(JobRepository jobRepository, PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
return new JobBuilder("personJob", jobRepository)
.start(new StepBuilder("step1", jobRepository)
.<Person, Person>chunk(200, transactionManager)
.reader(itemReader())
.writer(itemWriter())
.build())
.build();
}包含需要远程 Chunking 的 Step 的 Job 在 XML 中的配置可能与以下类似
<job id="personJob">
<step id="step1">
<tasklet>
<chunk reader="itemReader" writer="itemWriter" commit-interval="200"/>
</tasklet>
...
</step>
</job>ItemReader 引用指向您希望在管理器上用于读取数据的 bean。ItemWriter 引用指向一个特殊的 ItemWriter(称为 ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter),如前所述。处理器(如果有)被排除在管理器配置之外,因为它在 worker 上配置。在实现您的用例时,您应检查任何其他组件属性,例如节流限制等。
-
Java
-
XML
以下 Java 配置提供了基本的管理器设置
@Bean
public org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
ActiveMQConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory();
factory.setBrokerURL("tcp://:61616");
return factory;
}
/*
* Configure outbound flow (requests going to workers)
*/
@Bean
public DirectChannel requests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(requests())
.handle(Jms.outboundAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("requests"))
.get();
}
/*
* Configure inbound flow (replies coming from workers)
*/
@Bean
public QueueChannel replies() {
return new QueueChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow inboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("replies"))
.channel(replies())
.get();
}
/*
* Configure the ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter
*/
@Bean
public ItemWriter<Integer> itemWriter() {
MessagingTemplate messagingTemplate = new MessagingTemplate();
messagingTemplate.setDefaultChannel(requests());
messagingTemplate.setReceiveTimeout(2000);
ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter<Integer> chunkMessageChannelItemWriter
= new ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter<>();
chunkMessageChannelItemWriter.setMessagingOperations(messagingTemplate);
chunkMessageChannelItemWriter.setReplyChannel(replies());
return chunkMessageChannelItemWriter;
}以下 XML 配置提供了基本的管理器设置
<bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory">
<property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://:61616"/>
</bean>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter id="jmsRequests" destination-name="requests"/>
<bean id="messagingTemplate"
class="org.springframework.integration.core.MessagingTemplate">
<property name="defaultChannel" ref="requests"/>
<property name="receiveTimeout" value="2000"/>
</bean>
<bean id="itemWriter"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.chunk.ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter"
scope="step">
<property name="messagingOperations" ref="messagingTemplate"/>
<property name="replyChannel" ref="replies"/>
</bean>
<int:channel id="replies">
<int:queue/>
</int:channel>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter id="jmsReplies"
destination-name="replies"
channel="replies"/>前面的配置为我们提供了一些 bean。我们使用 ActiveMQ 以及 Spring Integration 提供的入站和出站 JMS 适配器来配置我们的消息中间件。如所示,我们的 itemWriter bean(由我们的 job step 引用)使用 ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter 通过配置的中间件写入 Chunk。
现在我们可以继续进行 worker 配置,如下例所示
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了 Java 中的 worker 配置
@Bean
public org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
ActiveMQConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory();
factory.setBrokerURL("tcp://:61616");
return factory;
}
/*
* Configure inbound flow (requests coming from the manager)
*/
@Bean
public DirectChannel requests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow inboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("requests"))
.channel(requests())
.get();
}
/*
* Configure outbound flow (replies going to the manager)
*/
@Bean
public DirectChannel replies() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(replies())
.handle(Jms.outboundAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("replies"))
.get();
}
/*
* Configure the ChunkProcessorChunkHandler
*/
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "requests", outputChannel = "replies")
public ChunkProcessorChunkHandler<Integer> chunkProcessorChunkHandler() {
ChunkProcessor<Integer> chunkProcessor
= new SimpleChunkProcessor<>(itemProcessor(), itemWriter());
ChunkProcessorChunkHandler<Integer> chunkProcessorChunkHandler
= new ChunkProcessorChunkHandler<>();
chunkProcessorChunkHandler.setChunkProcessor(chunkProcessor);
return chunkProcessorChunkHandler;
}以下示例展示了 XML 中的 worker 配置
<bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory">
<property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://:61616"/>
</bean>
<int:channel id="requests"/>
<int:channel id="replies"/>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter id="incomingRequests"
destination-name="requests"
channel="requests"/>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter id="outgoingReplies"
destination-name="replies"
channel="replies">
</int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter>
<int:service-activator id="serviceActivator"
input-channel="requests"
output-channel="replies"
ref="chunkProcessorChunkHandler"
method="handleChunk"/>
<bean id="chunkProcessorChunkHandler"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.chunk.ChunkProcessorChunkHandler">
<property name="chunkProcessor">
<bean class="org.springframework.batch.core.step.item.SimpleChunkProcessor">
<property name="itemWriter">
<bean class="io.spring.sbi.PersonItemWriter"/>
</property>
<property name="itemProcessor">
<bean class="io.spring.sbi.PersonItemProcessor"/>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>这些配置项中的大多数应该看起来与管理器配置相似。Worker 不需要访问 Spring Batch JobRepository 或实际的 job 配置文件。主要的关注 bean 是 chunkProcessorChunkHandler。ChunkProcessorChunkHandler 的 chunkProcessor 属性接受一个配置好的 SimpleChunkProcessor,您可以在其中提供对您的 ItemWriter(以及可选的 ItemProcessor)的引用,当 worker 从管理器接收到 Chunk 时,这些组件将在 worker 上运行。
有关更多信息,请参阅“可伸缩性”章节中关于远程 Chunking 的部分。
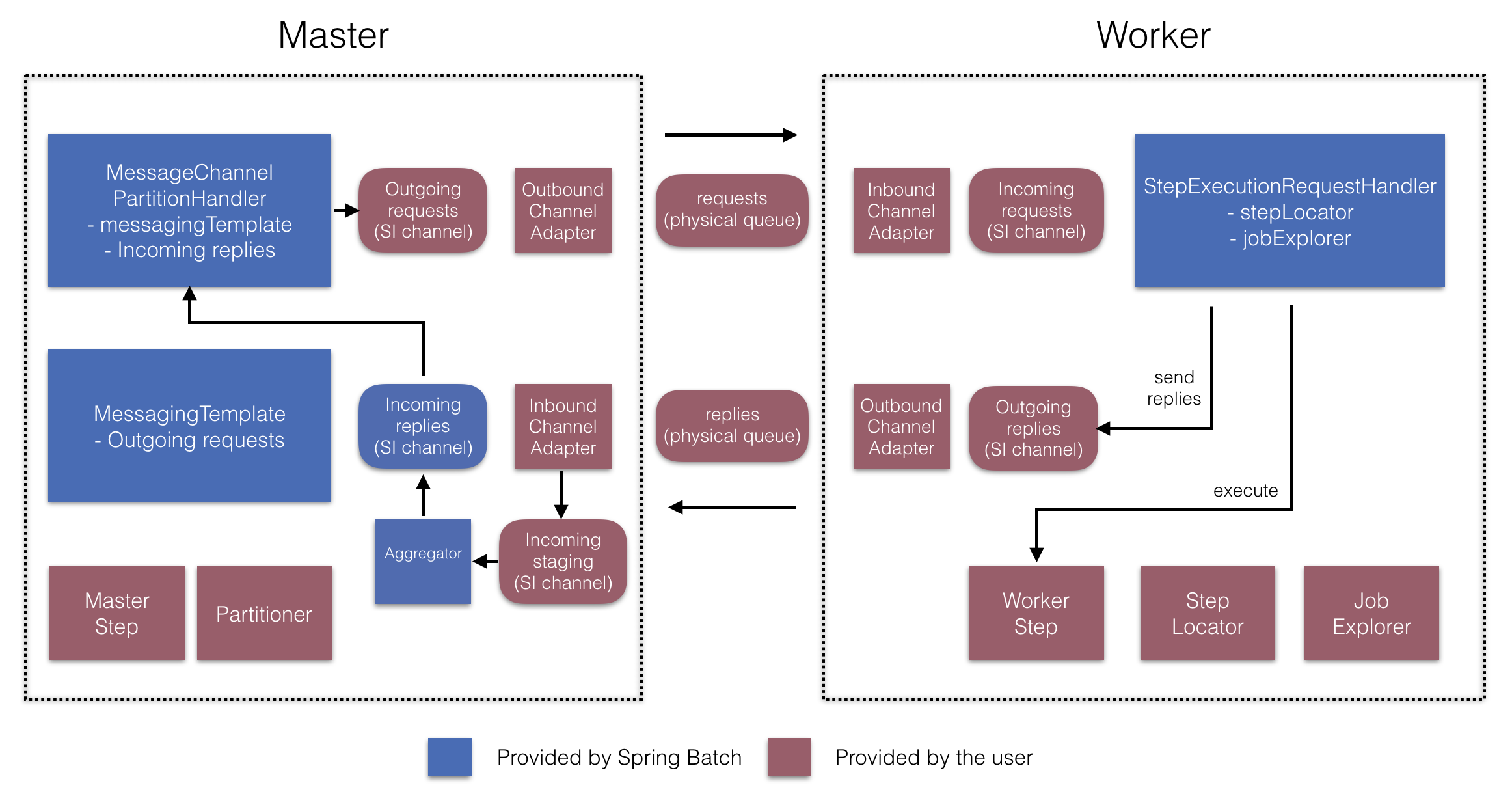
从版本 4.1 开始,Spring Batch Integration 引入了 @EnableBatchIntegration 注解,可用于简化远程 Chunking 设置。此注解提供了两个可以在您的应用程序上下文中自动装配的 bean:
-
RemoteChunkingManagerStepBuilderFactory: 配置管理器 Step -
RemoteChunkingWorkerBuilder: 配置远程 worker 集成流程
这些 API 负责配置许多组件,如下图所示
在管理器端,RemoteChunkingManagerStepBuilderFactory 允许您通过声明以下内容来配置管理器 Step:
-
用于读取 Item 并将其发送给 worker 的 Item Reader
-
用于向 worker 发送请求的出站通道(“Outgoing requests”)
-
用于接收 worker 回复的入站通道(“Incoming replies”)
您无需显式配置 ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter 和 MessagingTemplate。(如果您有理由这样做,仍然可以显式配置它们)。
在 worker 端,RemoteChunkingWorkerBuilder 允许您配置 worker 以:
-
监听管理器在入站通道(“Incoming requests”)上发送的请求
-
使用配置好的
ItemProcessor和ItemWriter对每个请求调用ChunkProcessorChunkHandler的handleChunk方法 -
在出站通道(“Outgoing replies”)上向管理器发送回复
您无需显式配置 SimpleChunkProcessor 和 ChunkProcessorChunkHandler。(如果您有理由这样做,仍然可以显式配置它们)。
以下示例展示了如何使用这些 API
@EnableBatchIntegration
@EnableBatchProcessing
public class RemoteChunkingJobConfiguration {
@Configuration
public static class ManagerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemoteChunkingManagerStepBuilderFactory managerStepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public TaskletStep managerStep() {
return this.managerStepBuilderFactory.get("managerStep")
.chunk(100)
.reader(itemReader())
.outputChannel(requests()) // requests sent to workers
.inputChannel(replies()) // replies received from workers
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
@Configuration
public static class WorkerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemoteChunkingWorkerBuilder workerBuilder;
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow workerFlow() {
return this.workerBuilder
.itemProcessor(itemProcessor())
.itemWriter(itemWriter())
.inputChannel(requests()) // requests received from the manager
.outputChannel(replies()) // replies sent to the manager
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
}您可以在此处找到远程 Chunking Job 的完整示例。
远程 Partitioning
下图展示了典型的远程 Partitioning 情况
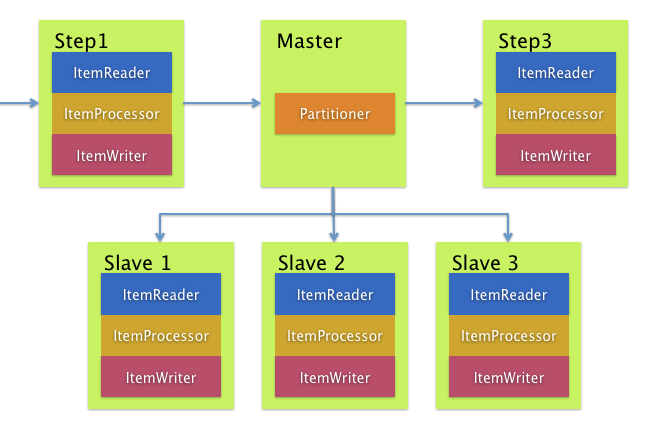
另一方面,远程 Partitioning 在不是 Item 处理而是相关的 I/O 导致瓶颈时很有用。使用远程 Partitioning,您可以将工作发送给执行完整 Spring Batch Step 的 worker。因此,每个 worker 都有自己的 ItemReader、ItemProcessor 和 ItemWriter。为此,Spring Batch Integration 提供了 MessageChannelPartitionHandler。
PartitionHandler 接口的此实现使用 MessageChannel 实例向远程 worker 发送指令并接收其响应。这提供了一个很好的抽象,使其与用于与远程 worker 通信的传输方式(如 JMS 和 AMQP)分离。
“可伸缩性”章节中讨论远程 Partitioning 的部分概述了配置远程 Partitioning 所需的概念和组件,并展示了使用默认 TaskExecutorPartitionHandler 在单独的本地执行线程中进行 Partitioning 的示例。对于到多个 JVM 的远程 Partitioning,还需要两个额外的组件:
-
一个远程调用框架或网格环境
-
支持所需的远程调用框架或网格环境的
PartitionHandler实现
与远程 Chunking 类似,您可以使用 JMS 作为“远程调用框架”。在这种情况下,如前所述,使用 MessageChannelPartitionHandler 实例作为 PartitionHandler 实现。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例假设存在一个已 Partitioning 的 Job,并重点介绍 Java 中的 MessageChannelPartitionHandler 和 JMS 配置
/*
* Configuration of the manager side
*/
@Bean
public PartitionHandler partitionHandler() {
MessageChannelPartitionHandler partitionHandler = new MessageChannelPartitionHandler();
partitionHandler.setStepName("step1");
partitionHandler.setGridSize(3);
partitionHandler.setReplyChannel(outboundReplies());
MessagingTemplate template = new MessagingTemplate();
template.setDefaultChannel(outboundRequests());
template.setReceiveTimeout(100000);
partitionHandler.setMessagingOperations(template);
return partitionHandler;
}
@Bean
public QueueChannel outboundReplies() {
return new QueueChannel();
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel outboundRequests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundJmsRequests() {
return IntegrationFlow.from("outboundRequests")
.handle(Jms.outboundGateway(connectionFactory())
.requestDestination("requestsQueue"))
.get();
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "inboundStaging")
public AggregatorFactoryBean partitioningMessageHandler() throws Exception {
AggregatorFactoryBean aggregatorFactoryBean = new AggregatorFactoryBean();
aggregatorFactoryBean.setProcessorBean(partitionHandler());
aggregatorFactoryBean.setOutputChannel(outboundReplies());
// configure other propeties of the aggregatorFactoryBean
return aggregatorFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel inboundStaging() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow inboundJmsStaging() {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory())
.configureListenerContainer(c -> c.subscriptionDurable(false))
.destination("stagingQueue"))
.channel(inboundStaging())
.get();
}
/*
* Configuration of the worker side
*/
@Bean
public StepExecutionRequestHandler stepExecutionRequestHandler() {
StepExecutionRequestHandler stepExecutionRequestHandler = new StepExecutionRequestHandler();
stepExecutionRequestHandler.setJobExplorer(jobExplorer);
stepExecutionRequestHandler.setStepLocator(stepLocator());
return stepExecutionRequestHandler;
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "inboundRequests", outputChannel = "outboundStaging")
public StepExecutionRequestHandler serviceActivator() throws Exception {
return stepExecutionRequestHandler();
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel inboundRequests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
public IntegrationFlow inboundJmsRequests() {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory())
.configureListenerContainer(c -> c.subscriptionDurable(false))
.destination("requestsQueue"))
.channel(inboundRequests())
.get();
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel outboundStaging() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundJmsStaging() {
return IntegrationFlow.from("outboundStaging")
.handle(Jms.outboundGateway(connectionFactory())
.requestDestination("stagingQueue"))
.get();
}以下示例假设存在一个已 Partitioning 的 Job,并重点介绍 XML 中的 MessageChannelPartitionHandler 和 JMS 配置
<bean id="partitionHandler"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.partition.MessageChannelPartitionHandler">
<property name="stepName" value="step1"/>
<property name="gridSize" value="3"/>
<property name="replyChannel" ref="outbound-replies"/>
<property name="messagingOperations">
<bean class="org.springframework.integration.core.MessagingTemplate">
<property name="defaultChannel" ref="outbound-requests"/>
<property name="receiveTimeout" value="100000"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<int:channel id="outbound-requests"/>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter destination="requestsQueue"
channel="outbound-requests"/>
<int:channel id="inbound-requests"/>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter destination="requestsQueue"
channel="inbound-requests"/>
<bean id="stepExecutionRequestHandler"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.partition.StepExecutionRequestHandler">
<property name="jobExplorer" ref="jobExplorer"/>
<property name="stepLocator" ref="stepLocator"/>
</bean>
<int:service-activator ref="stepExecutionRequestHandler" input-channel="inbound-requests"
output-channel="outbound-staging"/>
<int:channel id="outbound-staging"/>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter destination="stagingQueue"
channel="outbound-staging"/>
<int:channel id="inbound-staging"/>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter destination="stagingQueue"
channel="inbound-staging"/>
<int:aggregator ref="partitionHandler" input-channel="inbound-staging"
output-channel="outbound-replies"/>
<int:channel id="outbound-replies">
<int:queue/>
</int:channel>
<bean id="stepLocator"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.partition.BeanFactoryStepLocator" />您还必须确保 Partition 的 handler 属性映射到 partitionHandler bean。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何将 Java 中的 Partition handler 属性映射到 partitionHandler
public Job personJob(JobRepository jobRepository) {
return new JobBuilder("personJob", jobRepository)
.start(new StepBuilder("step1.manager", jobRepository)
.partitioner("step1.worker", partitioner())
.partitionHandler(partitionHandler())
.build())
.build();
}以下示例展示了如何将 XML 中的 Partition handler 属性映射到 partitionHandler
<job id="personJob">
<step id="step1.manager">
<partition partitioner="partitioner" handler="partitionHandler"/>
...
</step>
</job>您可以在此处找到远程 Partitioning Job 的完整示例。
您可以使用 @EnableBatchIntegration 注解来简化远程 Partitioning 设置。此注解提供了两个对远程 Partitioning 有用的 bean:
-
RemotePartitioningManagerStepBuilderFactory: 配置管理器 Step -
RemotePartitioningWorkerStepBuilderFactory: 配置 worker Step
这些 API 负责配置许多组件,如下图所示
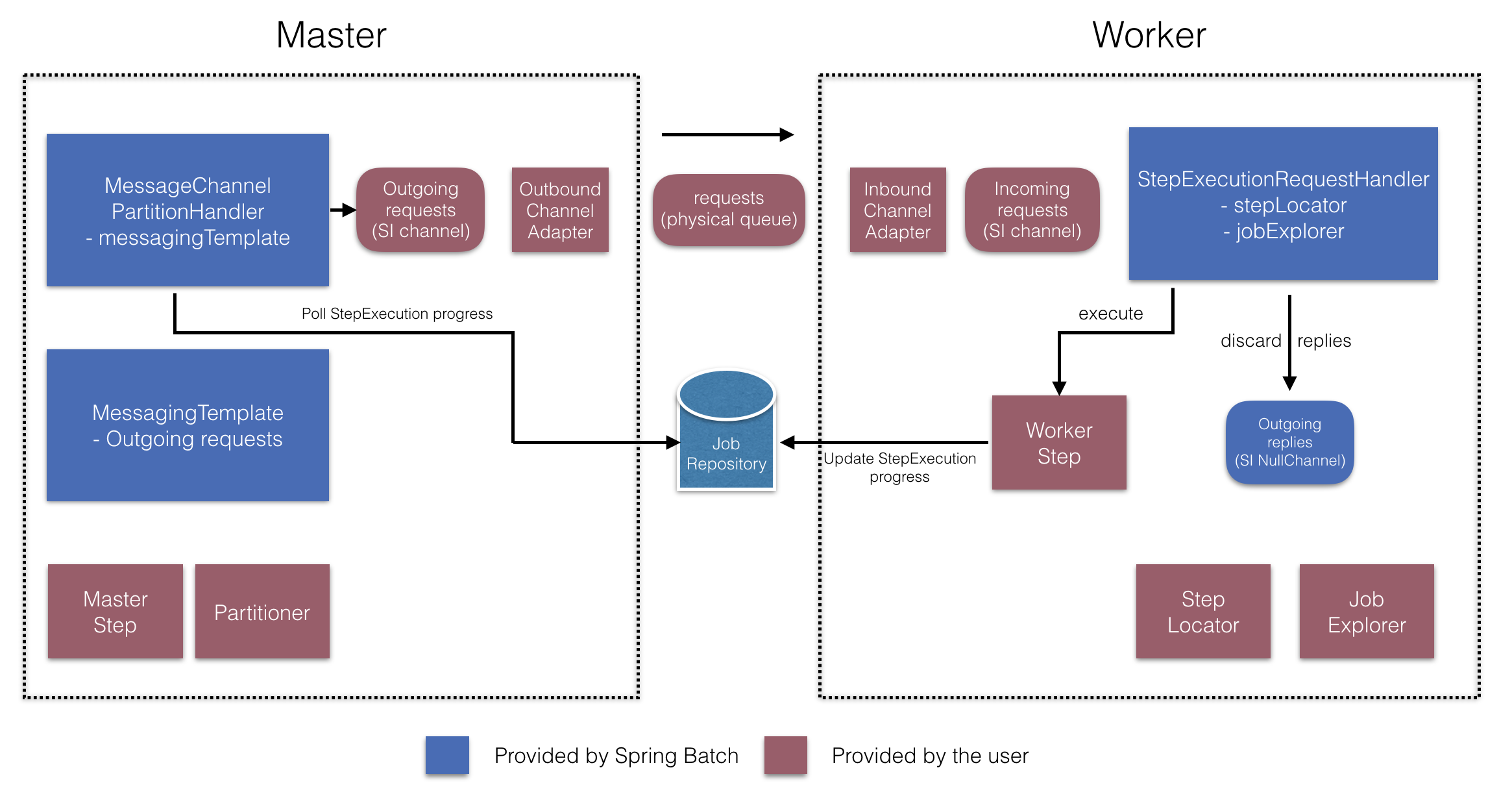
在管理器端,RemotePartitioningManagerStepBuilderFactory 允许您通过声明以下内容来配置管理器 Step:
-
用于 Partition 数据的
Partitioner -
用于向 worker 发送请求的出站通道(“Outgoing requests”)
-
用于接收 worker 回复的入站通道(“Incoming replies”)(配置回复聚合时)
-
轮询间隔和超时参数(配置 Job 仓库轮询时)
您无需显式配置 MessageChannelPartitionHandler 和 MessagingTemplate。(如果您有理由这样做,仍然可以显式配置它们)。
在 worker 端,RemotePartitioningWorkerStepBuilderFactory 允许您配置 worker 以:
-
监听管理器在入站通道(“Incoming requests”)上发送的请求
-
对每个请求调用
StepExecutionRequestHandler的handle方法 -
在出站通道(“Outgoing replies”)上向管理器发送回复
您无需显式配置 StepExecutionRequestHandler。(如果您有理由这样做,仍然可以显式配置它)。
以下示例展示了如何使用这些 API
@Configuration
@EnableBatchProcessing
@EnableBatchIntegration
public class RemotePartitioningJobConfiguration {
@Configuration
public static class ManagerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemotePartitioningManagerStepBuilderFactory managerStepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public Step managerStep() {
return this.managerStepBuilderFactory
.get("managerStep")
.partitioner("workerStep", partitioner())
.gridSize(10)
.outputChannel(outgoingRequestsToWorkers())
.inputChannel(incomingRepliesFromWorkers())
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
@Configuration
public static class WorkerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemotePartitioningWorkerStepBuilderFactory workerStepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public Step workerStep() {
return this.workerStepBuilderFactory
.get("workerStep")
.inputChannel(incomingRequestsFromManager())
.outputChannel(outgoingRepliesToManager())
.chunk(100)
.reader(itemReader())
.processor(itemProcessor())
.writer(itemWriter())
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
}
