使用外部仓库中的契约进行消费者驱动契约
在此流程中,我们执行消费者驱动的契约测试。契约定义存储在单独的仓库中。
先决条件
要将消费者驱动契约与外部仓库中的契约一起使用,您需要设置一个 Git 仓库,该仓库需要满足以下条件:
-
包含每个生产者的所有契约定义。
-
可以将契约定义打包成 JAR。
-
对于每个契约生产者,包含一种通过 Spring Cloud Contract 插件(SCC 插件)在本地安装存根的方式(例如,
pom.xml)。
您还需要设置了 Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner 的消费者代码。有关此类项目的示例,请参阅此示例。您还需要设置了 Spring Cloud Contract 和插件的生产者代码。有关此类项目的示例,请参阅此示例。存根存储是 Nexus 或 Artifactory。
在高层,流程如下:
-
消费者使用单独仓库中的契约定义。
-
消费者完成工作后,在消费者端创建一个包含工作代码的分支,并向保存契约定义的单独仓库发起拉取请求。
-
生产者接管对保存契约定义的单独仓库的拉取请求,并在本地安装包含所有契约的 JAR。
-
生产者从本地存储的 JAR 生成测试,并编写缺失的实现以使测试通过。
-
生产者完成工作后,合并对保存契约定义的仓库的拉取请求。
-
CI 工具构建包含契约定义的仓库并将包含契约定义的 JAR 上传到 Nexus 或 Artifactory 后,生产者可以合并其分支。
-
最后,消费者可以切换到在线工作以从远程位置获取生产者的存根,并且可以将分支合并到主分支。
消费者流程
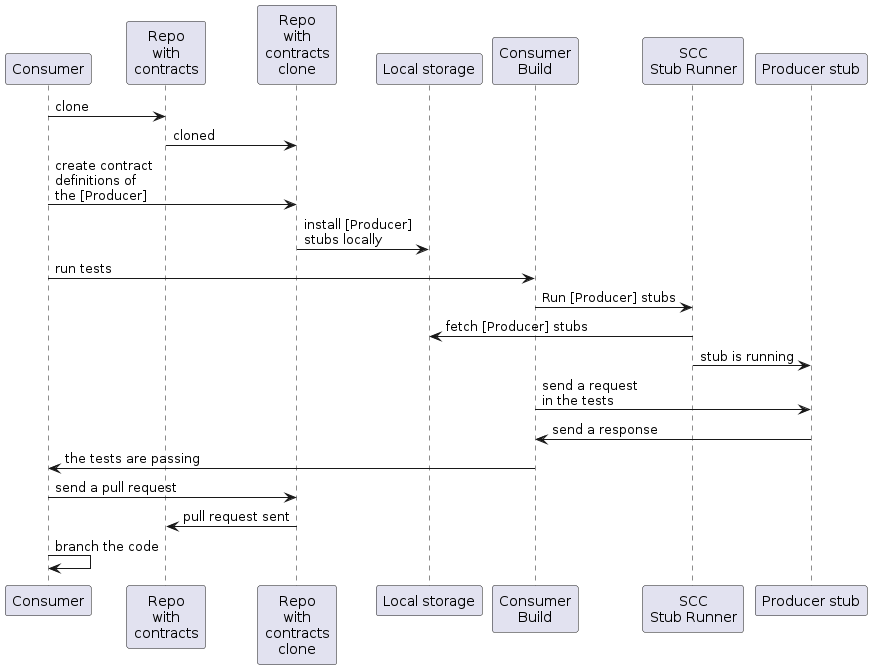
消费者
-
编写一个会向生产者发送请求的测试。
由于没有服务器,测试失败。
-
克隆保存契约定义的仓库。
-
在文件夹下将需求设置为契约,以消费者名称作为生产者的子文件夹。
例如,对于名为
producer的生产者和名为consumer的消费者,契约将存储在src/main/resources/contracts/producer/consumer/之下)。 -
定义契约后,将生产者存根安装到本地存储,示例如下:
$ cd src/main/resource/contracts/producer $ ./mvnw clean install -
在消费者测试中设置 Spring Cloud Contract (SCC) Stub Runner,以:
-
从本地存储获取生产者存根。
-
在“每消费者存根”模式下工作(这会启用消费者驱动契约模式)。
SCC Stub Runner
-
获取生产者存根。
-
运行一个带有生产者存根的内存 HTTP 服务器存根。现在您的测试与 HTTP 服务器存根通信,并且您的测试通过。
-
为生产者创建新的契约,并向包含契约定义的仓库发起拉取请求。
-
分支您的消费者代码,直到生产者团队合并其代码。
-
以下 UML 图显示了消费者流程:
生产者流程
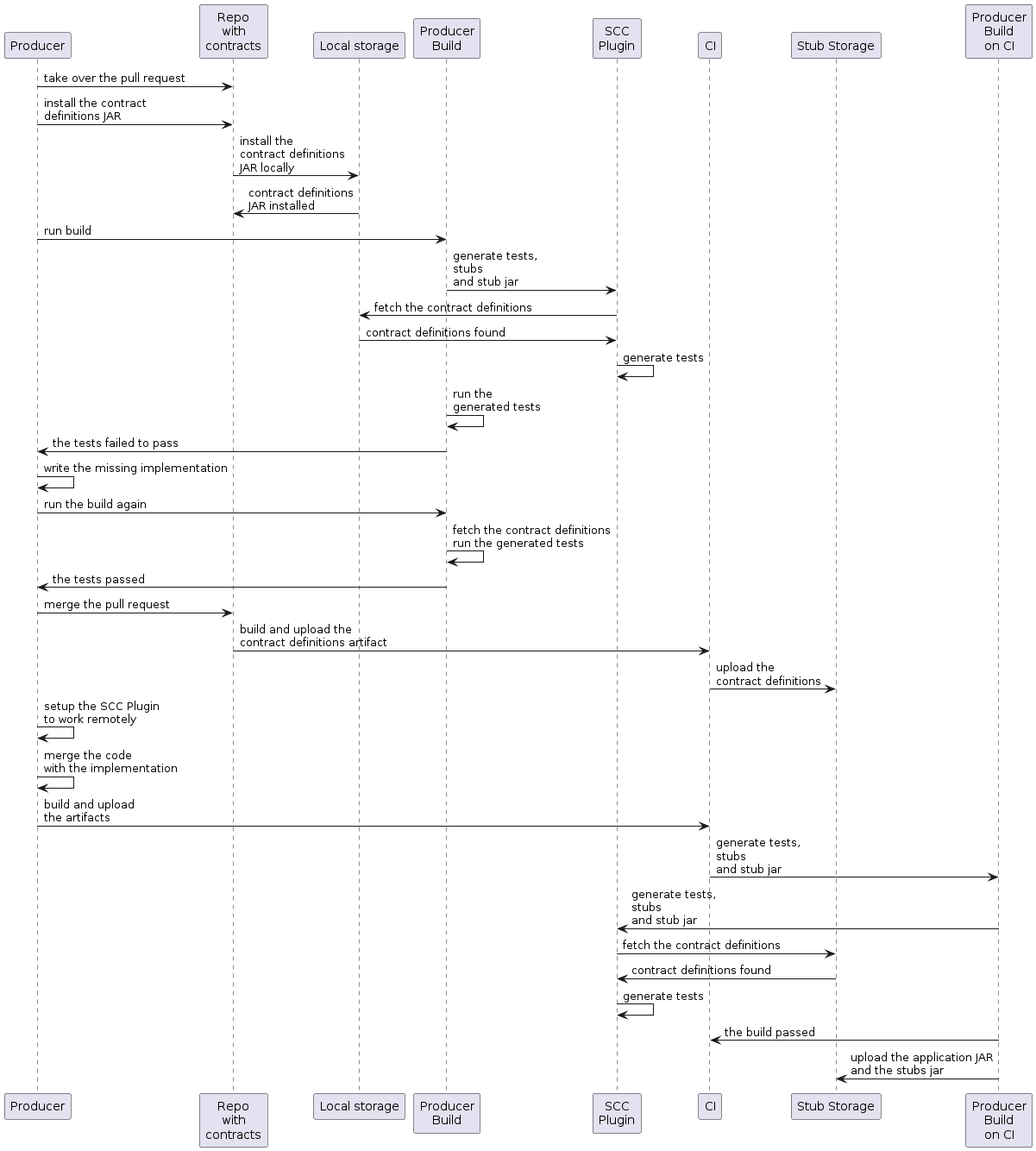
生产者
-
接管对保存契约定义的仓库的拉取请求。您可以从命令行执行此操作,如下所示:
$ git checkout -b the_branch_with_pull_request master git pull https://github.com/user_id/project_name.git the_branch_with_pull_request -
安装契约定义,如下所示:
$ ./mvnw clean install -
设置插件以从 JAR 而不是从
src/test/resources/contracts获取契约定义,如下所示:- Maven
-
<plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version> <extensions>true</extensions> <configuration> <!-- We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates --> <contractDependency> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>beer-contracts</artifactId> </contractDependency> <!-- The JAR with contracts should be taken from Maven local --> <contractsMode>LOCAL</contractsMode> <!-- ... additional configuration --> </configuration> </plugin> - Gradle
-
contracts { // We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates // group id `com.example`, artifact id `beer-contracts`, LATEST version and NO classifier contractDependency { stringNotation = 'com.example:beer-contracts:+:' } // The JAR with contracts should be taken from Maven local contractsMode = "LOCAL" // Additional configuration }
-
运行构建以生成测试和存根,如下所示:
- Maven
-
./mvnw clean install - Gradle
-
./gradlew clean build
-
编写缺失的实现,以使测试通过。
-
合并对保存契约定义的仓库的拉取请求,如下所示:
$ git commit -am "Finished the implementation to make the contract tests pass" $ git checkout master $ git merge --no-ff the_branch_with_pull_request $ git push origin masterCI 系统构建包含契约定义的项目,并将包含契约定义的 JAR 上传到 Nexus 或 Artifactory。
-
切换到远程工作。
-
设置插件,以便契约定义不再从本地存储而是从远程位置获取,如下所示:
- Maven
-
<plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version> <extensions>true</extensions> <configuration> <!-- We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates --> <contractDependency> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>beer-contracts</artifactId> </contractDependency> <!-- The JAR with contracts should be taken from a remote location --> <contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode> <!-- ... additional configuration --> </configuration> </plugin> - Gradle
-
contracts { // We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates // group id `com.example`, artifact id `beer-contracts`, LATEST version and NO classifier contractDependency { stringNotation = 'com.example:beer-contracts:+:' } // The JAR with contracts should be taken from a remote location contractsMode = "REMOTE" // Additional configuration }
-
将生产者代码与新实现合并。
-
CI 系统
-
构建项目。
-
生成测试、存根和存根 JAR。
-
将带有应用程序和存根的工件上传到 Nexus 或 Artifactory。
-
以下 UML 图显示了生产者流程: